
Kayakalpam (Rejuvenative) herbs: An immunomodulators in Siddha system ofmedicine: A scientific review
Carl Lewis John *, Leo Praveen Chelliah and Guru Prasad Chelliah
Agasthi Siddha Private Limited, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India.
Review Article
World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews, 2022, 13(02), 505–510
Article DOI: 10.30574/wjarr.2022.13.2.0167
DOI url: https://doi.org/10.30574/wjarr.2022.13.2.0167
Publication history:
Received on 15 January 2022; revised on 24 February 2022; accepted on 26 February 2022
Abstract:
Background: Kayakalpam (Rejuvenative) medicine is one of the prime treatment technique in the Siddha system of medicine. Kayakalpam has potential to heal, rejuvenate and balance the vatham, pitham and kapam (tri-dhosas) which make the body and mind to attain its stability. Several studies have been done on Kayakalpam medicines, but, this review article states about few Kayakalpam herbs, their chemical constituents, pharmacological activities and its immuno-modulatory mechanism towards the prevention and management of non-communicable diseases and several other diseases.
Methods: A literature review was conducted using the following scientific databases: PubMed, Research gate, Science Direct, Google scholar, Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India and Siddha Pharmacopoeia of India. The aim was to identify published data on traditionally used medicinal plant for rejuvenation and immuno-modulatory effect. From that, few Kayakalpam herbs have been chosen which has been mentioned in the Siddha literature and reviewed its nature.
Conclusion: This literature review reveals the potential effect of Kayakalpam herbs and its nature. Beyond any doubt it will help in prevention and management of non-communicable diseases and several other diseases.
Keywords:
Kayakalpam; Siddha System of Medicine; Rejuvenation; Immuno-modulator; Kayakalpam herbs; non-communicable diseases
Full text article in PDF: https://wjarr.com/sites/default/files/WJARR-2022-0167.pdf
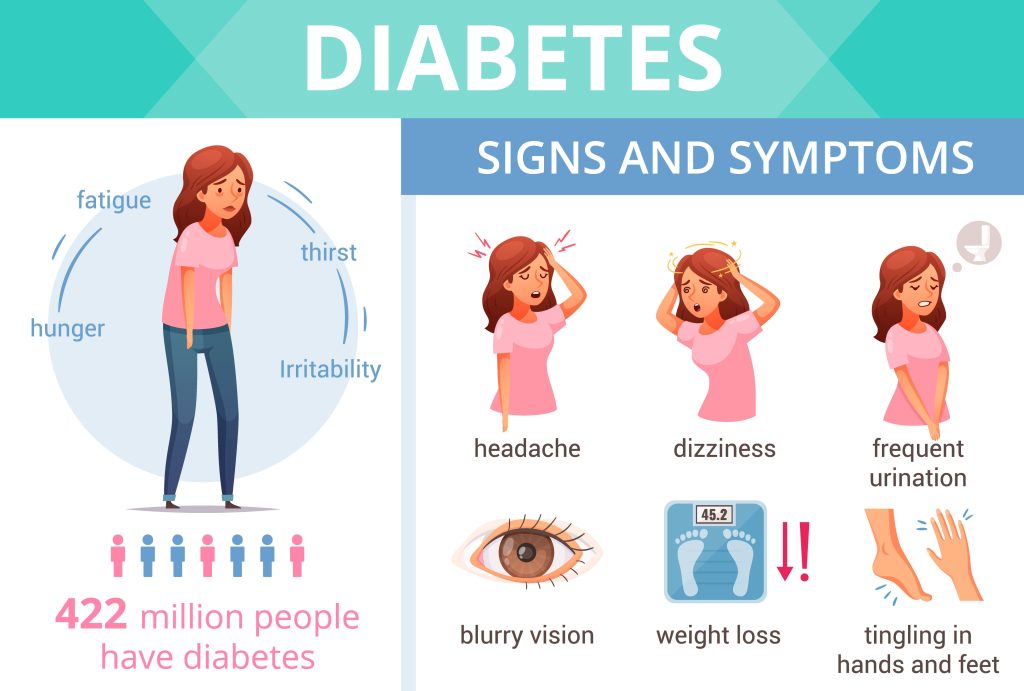
What are all the symptoms of diabetes?
Need to urinate often,
Thirst,
Constant hunger,
Weight loss,
Vision changes and
Fatigue. These symptoms may occur suddenly.
Symptoms for type 2 diabetes are generally similar to those of type 1 diabetes, but are often less marked. As a result, the disease may be diagnosed several years after onset, after complications have already arisen. For this reason, it is important to be aware of risk factors.

What is diabetes distress?
Diabetes distress is the emotional impact in diabetic individuals, which can include feelings of guilt, anxiety, and concerns about self-management of the condition. Living with diabetes involves variety of self-care behaviours such as medication adherence, healthy diet, and glucose monitoring. The continual duties of self-care, combined with a fear of complications, are the reason for this issue.
It is due to social (e.g., stigma, discrimination, or dealing with other people’s unhelpful reactions or lack of understanding) and financial difficulties that they face in their daily routine.
Low mood is one of the signs of diabetes distress. Diabetes distress differs from other types of distress, such as depression, which is also common among diabetics. It is not classified as a mental disease. Diabetes distress is widespread and long-lasting, with prevalence estimates of more than 20% for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes distress is categorised into six domains: treatment regimen, food and eating, future and complications, hypoglycemia, social and interpersonal relationships, and interactions with health-care professionals.

Tisanes / Herbal tea
HERBAL TEA
Herbal teas can contain herbs, flowers, spices, roots, fruits. Non-tea beverage is appropriately known as tisane, or simply herbal infusion. The majority of the herbs in our herbal teas have been used medicinally for decades. Herbal cures include classics like nausea-relieving ginger and sleep-inducing Ashwagantha, as well as more exotic flavours like lemongrass, a blue butterfly pea that creates a blue and wonderfully flowery elixir that is at least as antioxidant-rich as any tea while being naturally caffeine-free.
There are two basic processes to the production of herbal tea.
Non fermented tea.
Picking, withering, blanching, rolling, and drying are the most common methods for producing non-fermented herbal teas.
Fermented tea.
Fermented tea is a minor component of herbal tea and is mostly prepared by plucking, withering, rolling, fermenting, and drying.
According to epidemiological research, using tisanes reduces the incidence of type 2 diabetes and associated consequences. This link is ascribed to a range of factors, including activating the insulin signalling system, improving insulin resistance, reducing inflammation, enhancing insulin action, protecting islet β-cells, and scavenging free radicals.
Herbal tea is a healthy beverage with traditional therapeutic benefits. Tisanes exhibit several biological functions, such as mending injured β-cells, enhancing insulin sensitivity, and reducing diabetic complications.
Herbal teas vary widely in substance; they are made from natural components, mostly herbs, and have a variety of health benefits. Herbal teas can be brewed using fresh or dried roots, stems, leaves, fruits, flowers, seeds, bark, or whole plants of one or more plant species. Herbal tea differs from normal tea (Camellia) in that it is made by brewing or boiling plant components.
Some herbal teas, such as leaf tea, flower tea, and fruit tea, created with green tea technology, can be prepared by simply soaking in cold water.
Regular herbal tea consumption has been linked to lower incidences of T2DM and serum glucose levels in diabetic patients.
According to research, limiting oxidation early in tea processing can result in a high concentration of polyphenols, which are potent antioxidants with several health benefits. Herbal tea is an important part of tea culture since it complements tea intake and is used to promote health and offer healthcare.

